What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that causes the deterioration of the blood vessels in the retina because of high levels of blood sugar. Diabetes is a condition that causes a higher level of blood sugar than normal because the body is unable to properly use and store the sugar.

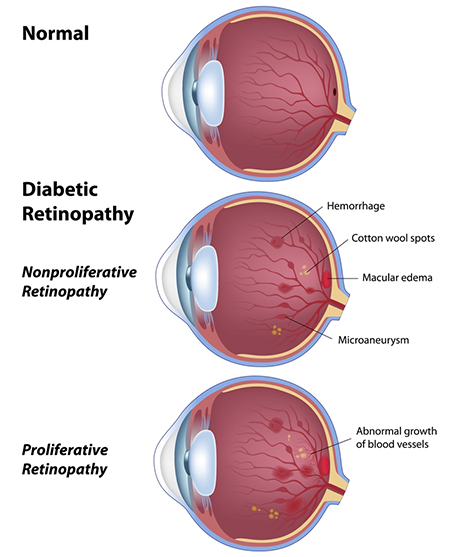
What Are the Types of Diabetic Retinopathy and what’s The Difference?
There are two types of diabetic retinopathy:
Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
This is the more common form. New blood vessels aren’t growing. Instead, the walls of the blood vessels in the retina weaken. Smaller vessels may develop bulges that can leak blood and other fluid into the retina. Larger vessels can become irregular in diameter. This early form of diabetic retinopathy can progress to the advanced form as more blood vessels become blocked.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
In this more severe form of retinopathy, damaged blood vessels close off, instigating the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels in the retina. These can leak into the vitreous, the jelly-like filling of the center of the eye. Scar tissue will often form due to the new blood vessel growth, and this can cause the retina to detach from the back of the eye.
The abnormal blood vessels may also interfere with the flow of fluid out of the eye, increasing pressure in the eyeball. This is glaucoma and the increased pressure can damage the optic nerve.
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Patients with diabetic retinopathy may not experience any changes in vision, so it is important for those with diabetes to have regular eye exams. Georgina Eye Clinic provides eye examinations at all of our locations across Kampala.
The most common symptoms experienced are: blurred vision, sudden and severe loss in vision, rings around lights, dark spots, or flashing lights. If you notice any of these symptoms call North Suburban Eye Associates to schedule an appointment.
What Are The Four Stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy has four distinct stages:
1. Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy
At this stage, micro aneurysms occur. They are small areas of balloon-like swelling in the retina’s tiny blood vessels. These do not affect vision and often go unnoticed.
2. Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy
Now the blood vessels that nourish the retina are blocked. This will often cause visible changes in the retina.
3. Severe Nonproliferative Retinopathy
In this stage, many more blood vessels are blocked, depriving several areas of the retina of their blood supply. These areas of the retina send signals to the body to grow new blood vessels for nourishment.
4. Proliferative Retinopathy
The most advanced stage. Now, as the retina sends signals that it needs nourishment, new blood vessels are created, but they are abnormal and fragile. They grow along the retina and along the surface of the clear, vitreous gel that fills the inside of the eye. The vessels aren’t the problem, as alone they don’t cause any symptoms or vision loss. The problem is their thin, fragile walls. These leak blood and can lead to severe vision loss and even blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
For slight cases of diabetic retinopathy, treatment may not be necessary, but close monitoring for changes and progression is important. In more advanced cases laser photocoagulation may be performed.
During this surgery, our surgeons use a laser to generate a quick burst of light energy to treat the leaking blood vessels and reduce the abnormal blood vessels to prevent further bleeding and scarring. If the bleeding is severe a Vitrectomy may need to be performed to remove the blood from the center of the eye. Since diabetes continuously affects the body, these treatments will not cure diabetic retinopathy.
What Is Recovery Like After These Treatments?
With laser treatments, you may have some discomfort and your vision may be blurry for a day or two, but most patients can return to normal activities immediately after these treatments. Some patients experience flashes of light at night or when looking at anything with a white background. These issues will decrease and resolve.
With injections, your visual acuity will also be impacted, but will significantly improve within a week or two. Recovery varies between the different drugs injected.
Vitrectomy requires the most involved recovery, with full recovery taking between 4 to 6 weeks. Some patients may be required to lay face down for a period of time to help their eye heal properly. Typical activities such as driving, reading, and exercise will need to wait for at least a week, maybe more.
What Are The Risk Factors For Developing Diabetic Retinopathy?
If you have diabetes, you can develop diabetic retinopathy. These factors increase your risk:
- Longer duration having diabetes
- Poor control of your blood sugar levels
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Pregnancy
- Tobacco use
- Being African American, Hispanic, or Native American
Will I Need To Get Touch-Up Treatments After My Initial Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment?
Diabetes continues to affect the body, so the patient’s diabetic retinopathy isn’t cured. You’ll still need to see us for regular eye exams so we can keep an eye out for any new development of abnormal blood vessels and possible blood leakage.
After having one of the possible treatments, such as focal or scatter laser treatment or a vitrectomy, you shouldn’t think you can now forget about your diabetic retinopathy. You’ll need to remain vigilant to prevent further vision loss.
What Issues Can Diabetic Retinopathy Cause If Left Untreated?
These abnormal blood vessels may either bleed or leak fluid or grow on the surface of the retina causing bleeding and scarring. Both of these complications can result in permanent loss of vision.
Schedule A Consultation
To learn more about diabetic retinopathy and how we can help you, contact us at 0755 347258.
